Invivyd is not liable for the accuracy of the information in a site’s profile.
Invivyd, Inc. Infusion Center Locator Website Directory Terms and Conditions of Use Agreement
THIS CLICK-THROUGH AGREEMENT (THIS “AGREEMENT”) IS BETWEEN INVIVYD, INC. (INVIVYD) AND YOU. IF YOU ARE ENTERING INTO THIS AGREEMENT ON BEHALF OF A PHYSICIAN(S), PROFESSIONAL ORGANIZATION, COMPANY OR OTHER ENTITY, YOU REPRESENT THAT YOU ARE THE EMPLOYEE OR AGENT OF SUCH PHYSICIAN(S), PROFESSIONAL ORGANIZATION, COMPANY (OR OTHER ENTITY) AND YOU HAVE THE AUTHORITY TO ENTER INTO THIS AGREEMENT ON BEHALF OF SUCH PHYSICIAN(S), PROFESSIONAL ORGANIZATION, COMPANY (OR OTHER ENTITY). BY CLICKING ON THE “ACCEPT” BUTTON BELOW OR BY CHECKING THE BOX INDICATING YOUR ACCEPTANCE, YOU ACKNOWLEDGE THAT YOU HAVE READ ALL OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS SET FORTH BELOW, UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS AGREEMENT, AND AGREE TO BE BOUND BY ALL OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS AGREEMENT. BY USING THE Invivyd, Inc. Infusion Center Locator website Directory (the "LOCATOR" hereafter), you are acknowledging your consent to these Terms and Conditions of Use. Do not use the Locator if you do not agree to the following Terms and Conditions of Use. Invivyd reserves the right to modify these Terms and Conditions of Use from time to time.
IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO ANY OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS AGREEMENT, INVIVYD IS UNWILLING TO ALLOW YOU TO USE OR SEARCH THE LOCATOR.
THE “EFFECTIVE DATE” OF THIS AGREEMENT IS THE DATE UPON WHICH YOU CLICK THE “ACCEPT” BUTTON. FOR THE PURPOSE OF THIS AGREEMENT, YOU AND, IF APPLICABLE, SUCH PHYSICIAN(S), PROFESSIONAL ORGANIZATION, COMPANY (OR OTHER ENTITY) CONSTITUTES “USER”.
Terms of Service. Invivyd, Inc. (INVIVYD) maintains an infusion center website directory (the “Locator”) to help patients, providers, organizations and other interested parties find access to appropriate sites of care for infusion therapy of PEMGARDA (pemivibart) injection for intravenous use (Please see the Fact Sheet for Patients, Parents, and Caregivers). Upon acceptance of the terms herein, User may search the Locator. User desires to use the Locator only in accordance with the terms set forth herein.
License. INVIVYD grants to User a nonexclusive, nontransferable, nonsublicensable, revocable and limited license to access and use its Locator solely for the specific purpose of searching the Locator to locate infusions sites of care for patients.
License Restrictions. Unless expressly otherwise set forth in this Agreement, User will not use the Locator to (a) solicit, attempt to solicit, or contact with the intent to solicit any product or service, (b) modify, rent, reverse engineer, copy, replicate, create derivative works of, disseminate, or disassemble the Locator, (c) engage in or support commercial activities or enterprise of the user or user’s affiliates, or (d) cause or permit any other party to do any of the foregoing.
Ownership. As between the parties, INVIVYD owns all right, title and interest in and to the Locator. No implied licenses are granted or exist in this Agreement, and INVIVYD reserves all rights not expressly granted under this Agreement.
Possible Errors and Omissions. The information in the Locator may contain inaccuracies or typographical errors. Invivyd reserves the right to make additions, deletions or modification to the information within the Locator at any time without prior notice. Invivyd also reserves the right to withdraw any site or other information contained in the Locator. USER ASSUMES FULL RESPONSIBILITY OF ANY AND ALL RISKS ARISING FROM OR RELATED TO THE USE OF THE LOCATOR OR THE INFORMATION CONTAINED THEREIN.
Warranty and Disclaimer. INVIVYD expressly disclaims responsibility for any consequences or liability attributable to or related to any use, non-use, or interpretation of information contained or not contained in the Locator. User represents warrants and covenants that: (a) User and, as applicable, all of User’s employees and consultants will abide by the terms of this Agreement; and (b) User and, as applicable, all of User’s employees and consultants will comply with all applicable laws, regulations, rules, orders and other requirements, now or hereafter in effect, of any applicable regulatory or governmental authority, in its performance of this Agreement. Notwithstanding any terms to the contrary in this Agreement, User will remain responsible for acts or omissions of all employees or consultants of User to the same extent as if such acts or omissions were undertaken by User. THE LOCATOR IS PROVIDED ON AN “AS IS” OR “AS AVAILABLE” BASIS WITHOUT ANY REPRESENTATIONS, WARRANTIES, COVENANTS OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND. INVIVYD DOES NOT WARRANT OR REPRESENT THAT ANY PART OF THE LOCATOR WILL BE FREE FROM ALL ERRORS, OR OMISSIONS. INVIVYD DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL OTHER WARRANTIES AND REPRESENTATIONS (EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, ORAL OR WRITTEN, CREATED BY CONTRACT, OR OTHERWISE) WITH RESPECT TO THE LOCATOR WHETHER ALLEGED TO ARISE BY OPERATION OF LAW, BY REASON OF CUSTOM OR USAGE IN THE TRADE, BY COURSE OF DEALING OR OTHERWISE INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY AND ALL (I) WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, (II) WARRANTIES OF FITNESS OR SUITABILITY FOR ANY PURPOSE (WHETHER OR NOT INVIVYD KNOWS, HAS REASON TO KNOW, HAS BEEN ADVISED, OR IS OTHERWISE AWARE OF ANY SUCH PURPOSE), AND (III) WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT OR CONDITION OF TITLE. USER ACKNOWLEDGES AND AGREES THAT USER HAS RELIED ON NO WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS. IN NO EVENT SHALL INVIVYD BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, PUNITIVE, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING LOSS OF PROFIT) ARISING FROM OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR EXISTENCE OF THE LOCATOR, THE INABILITY TO USE THE LOCATOR, AND/OR THE INFORMATION THAT THE LOCATOR CONTAINS, REGARDLESS OF WHETHER INVIVYD HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. INVIVYD DOES NOT WARRANT THAT THE LOCATOR OR THE SERVERS THAT MAKE IT AVAILABLE ARE FREE FROM ERRORS OF ANY SORT OR FREE FROM COMPUTER VIRUSES.
INVIVYD ALSO DISCLAIMS RESPONSIBILITY FOR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER THAT RESULT FROM MISTAKES, OMISSIONS, INTERRUPTIONS, DELETION OF FILES, ERRORS, DEFECTS, DELAYS IN OPERATION OR TRANSMISSION, OR ANY FAILURE OF PERFORMANCE RELATING TO THE LOCATOR WHETHER OR NOT CAUSED BY EVENTS BEYOND OUR REASONABLE CONTROL INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ACTS OF ANY OF OUR THIRD-PARTY VENDORS, ACTS OF GOD, COMMUNICATION LINE FAILURE, THEFT, DESTRUCTION OR UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS TO THE WEBSITES’ RECORDS, PROGRAMS OR SERVICES. IN NO EVENT SHALL INVIVYD’S TOTAL LIABILITY FOR ALL DAMAGES, LOSSES AND CAUSES OF ACTION EXCEED FIVE DOLLARS ($5.00).
Indemnification. YOU AGREE TO DEFEND, INDEMNIFY, AND HOLD HARMLESS INVIVYD, ITS OFFICERS, DIRECTORS, EMPLOYEES AND THIRD-PARTY VENDORS FROM AND AGAINST ANY LOSSES, DAMAGES, CLAIMS, ACTIONS, DEMANDS OR EXPENSES, INCLUDING REASONABLE ATTORNEY’S FEES, OF ANY PERSON OR ENTITY, INCLUDING PERSONAL INJURY AND DEATH, REGARDLESS OF WHETHER THEY ARISE OUT OF OR ARE ATTRIBUTABLE TO ANY ACT OR OMISSION, NEGLIGENT OR OTHERWISE, OF INVIVYD, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH: (i) YOUR USE OF ANY OF THE LOCATOR, (ii) YOUR BREACH OF THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF USE, INCLUDING ANY ABUSIVE OR UNLAWFUL BEHAVIOR ON THE PART OF YOU OR YOUR DEPENDENTS, OR (iii) YOUR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OR PRIVACY RIGHT OF ANY PERSON. THIS INDEMNIFICATION PROVISION SHALL APPLY TO THIRD-PARTY CLAIMS AS WELL AS CLAIMS BETWEEN THE PARTIES TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF USE.
Use of Data. In compliance with applicable privacy rules, regulations and laws, (i) INVIVYD hereby expressly reserves the right to process and (2) User hereby grants INVIVYD the right to process, including without limitation, collect, use, analyze, record, organize, structure, store, adapt or alter, retrieve, consult, use, disclose by transmission, disseminate or otherwise make available, align or combine, restrict, erase or destroy and disseminate any and all User information and data including, but not limited to, your search queries, search results, search patterns, geography and demographic information, Locator usage date and time of search session(s), geographic location, how you navigated the Locator site, and how you interacted with the Locator site. This information is collected for our legitimate business purposes and will be saved for the period of time needed to fulfill legitimate and lawful business purposes in accordance with INVIVYD’s policies and applicable laws and regulations. User accepts that their personal information is treated in accordance with Invivyd's online Privacy Policy.
Limitation of Liability. EXCEPT FOR ANY ACTS OF FRAUD, GROSS NEGLIGENCE, OR WILLFUL MISCONDUCT, IN NO EVENT WILL INVIVYD BE LIABLE TO USER OR ANY THIRD PARTY FOR ANY LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF USE, LOSS OF REVENUE, LOSS OF GOODWILL, ANY INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS, OR FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, EXEMPLARY, PUNITIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THIS AGREEMENT OR THE LOCATOR, REGARDLESS OF THE TYPE OF ACTION, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT, STRICT LIABILITY OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF INVIVYD HAS BEEN ADVISED OR IS OTHERWISE AWARE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Termination. The term of this Agreement will commence on the Effective Date and will remain in effect in perpetuity, unless otherwise terminated in accordance with this Agreement. User may voluntarily terminate this Agreement at any time by deleting and destroying all physical and/or electronic copies of any part of the Locator. Without prejudice to any other rights, in the event of a breach of this Agreement by you, INVIVYD may immediately terminate this Agreement. Upon expiration or termination of this Agreement, all rights granted to User under this Agreement will immediately cease. In addition to all definitions and this sentence, the following sections will survive any termination or expiration of this Agreement: Warranty and Disclaimer, Indemnification, Use of Data, and Limitation of Liability.
Miscellaneous. This Agreement is the entire agreement of the parties regarding the subject matter hereof, superseding all other agreements between them, whether oral or written, regarding the subject matter hereof. This Agreement will be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of Massachusetts applicable to agreements made and to be entirely performed within the State of Massachusetts, without resort to its conflict of law provisions. User may not transfer User’s rights under this Agreement to any third party. If any provision of this Agreement is invalid, illegal, or incapable of being enforced by any rule of law or public policy, all other provisions of this Agreement will nonetheless remain in full force and effect.
If any of the above exclusions of warranties is unenforceable in your jurisdiction, the other exclusions listed above will still be given effect to the full extent permitted by that jurisdiction's law.


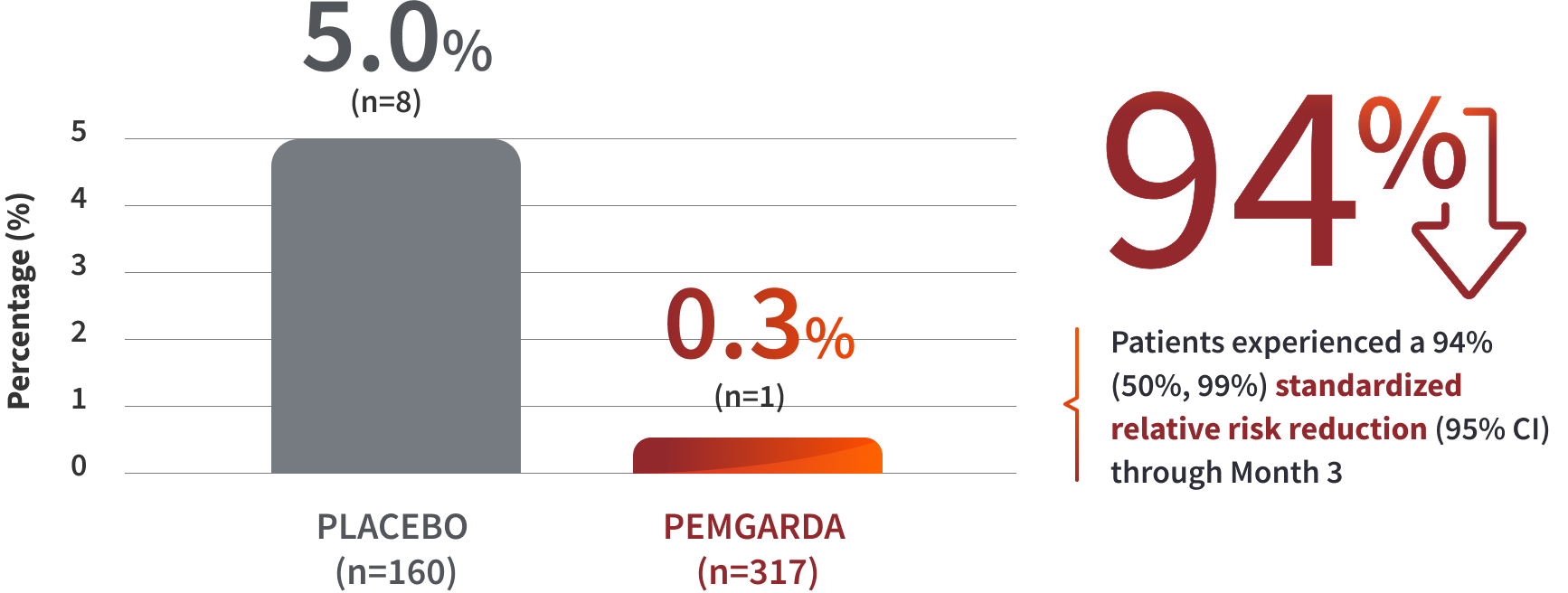
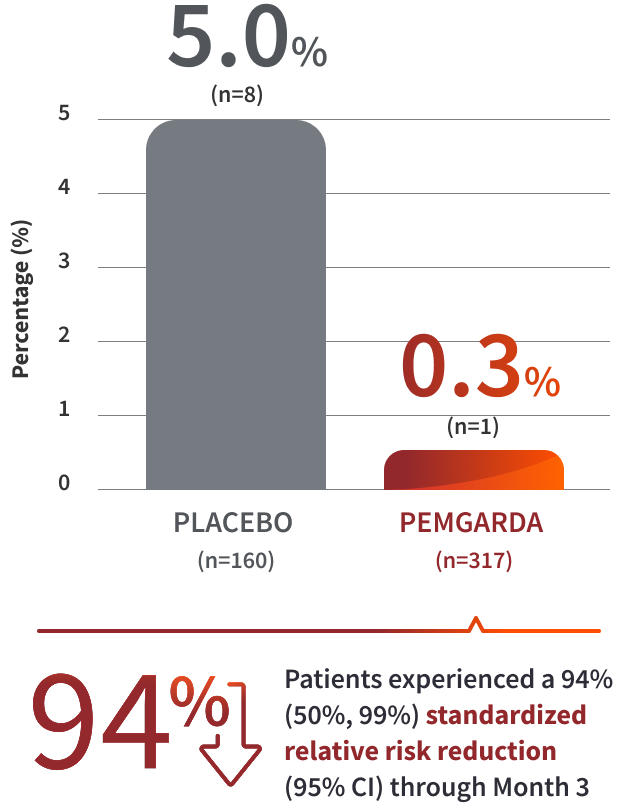
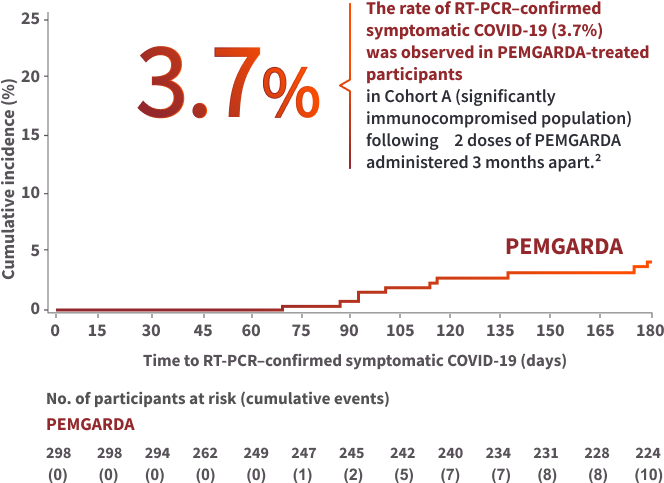
 COHORT A RESULTS
COHORT A RESULTS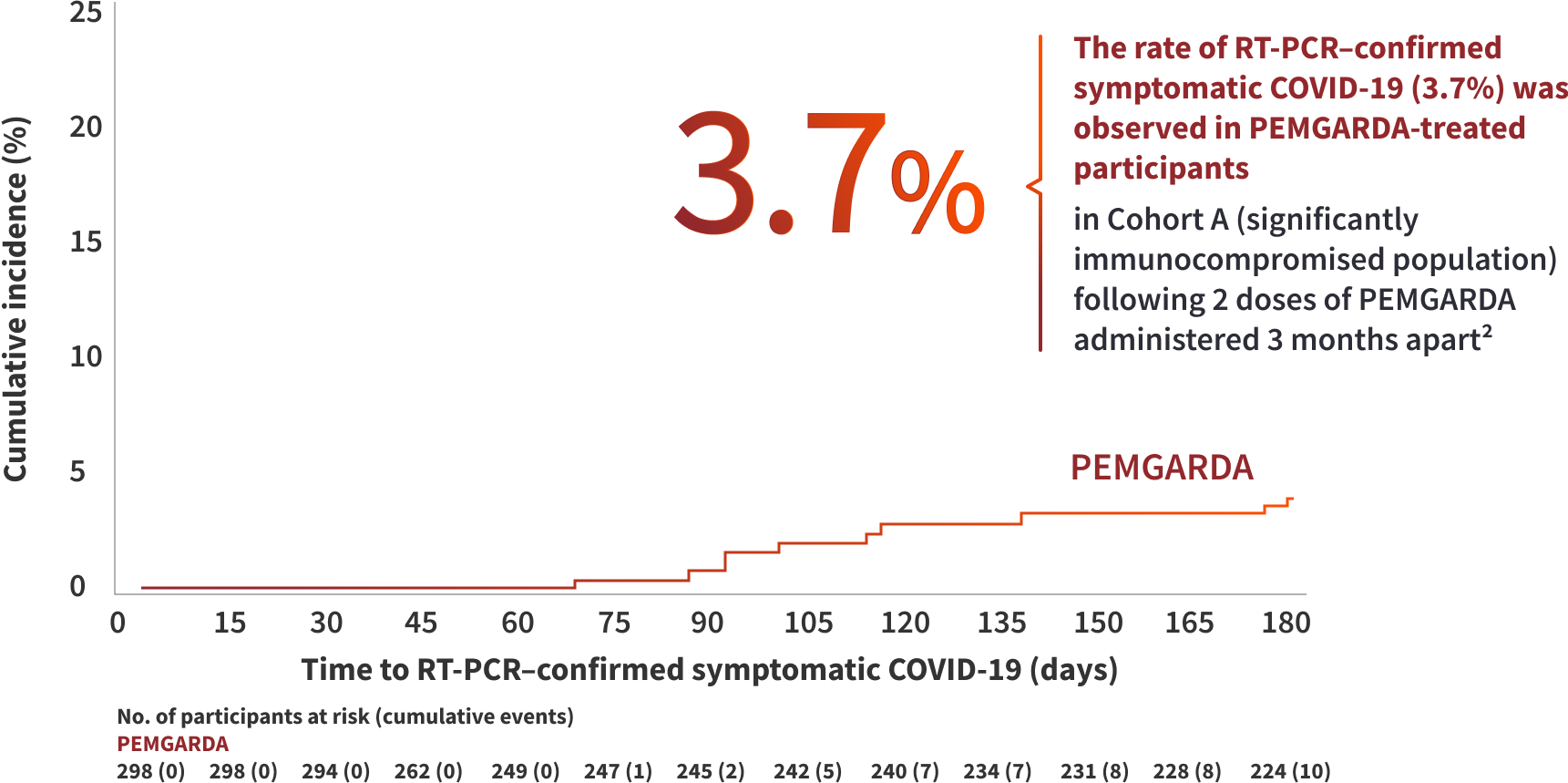
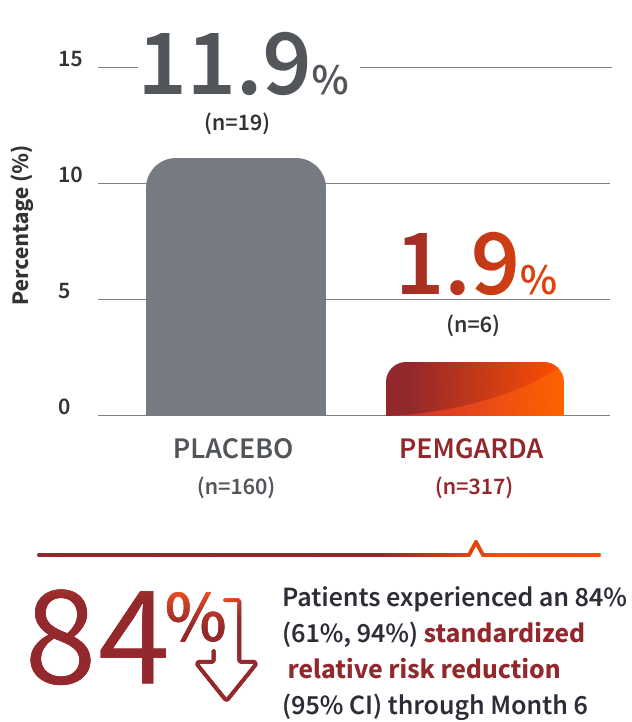
 COHORT B RESULTS
COHORT B RESULTS